What is a LAN
A LAN (Local Area Network) is a computers group that consists of several connected computers in an area. The area commonly is about thousands of meters. A LAN can achieve the targets, including Documents Management, Application Sharing, Printers Sharing, E-mail, and so on. The LAN is closed network that can consist of 2 PCs or thousands of PCs in one company.
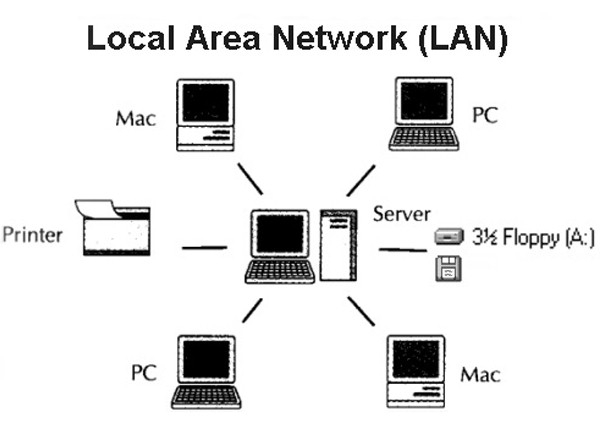
These hardware and software can build a LAN, including network hardware (network servers, network printers, network card, etc.), Network transmission media and Network software.
Features
The Local area network is generally owned by one department or unit. It is easy to build, maintain and expand, and the system flexibility is high.
Its main features have:
- The geographical coverage is small, only in a relatively independent local area within the joint, such as a centralized building.
- It uses the special laid transmission media for networking, delivering high data transfer rate (10Mbs - 10Gbs)
- Communication delay time is short. High reliability.
- LAN can support a variety of transmission media.
Topology
The LANs are usually distributed over a limited geographical area of the network system, generally involving the geographical range of only a few kilometers. LAN specialization is very strong, with a more stable and standardized topology.
The Common LAN topologies are as follows:
- Star Topology
A star topology is a topology for a Local Area Network (LAN) in which all nodes are individually connected to a central connection point, like a hub or a switch. A star takes more cable than e.g. a bus, but the benefit is that if a cable fails, only one node will be brought down.
- Tree Topology
A tree topology combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. It consists of groups of star-configured workstations connected to a linear bus backbone cable. Tree topologies allow for the expansion of an existing network, and enable schools to configure a network to meet their needs.
- Linear Bus Topology
A linear bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end. All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable.
- Ring Network
A ring network is a network topology in which each node connects to exactly two other nodes, forming a single continuous pathway for signals through each node - a ring. Data travels from node to node, with each node along the way handling every packet.
How to set up a Home LAN
This is a quick guide to setting up a simple LAN in your home.
- Gather your equipment
To set up a LAN, you need these devices:
- A network switch - or a router
- An ethernet cable, plus extra ones for every device you want to connect via cable
- A computer
- All the rest of your devices
If you want your LAN to connect to the internet, you'll also need:
- A broadband connection
- A router
- A modem (if there isn't one built in to your router)
- Connect the first computer
Use the Ethernet cable to connect the computer with the router or the switch.
On a Windows PC: Using a network switch or router for the first time should bring up the 'Set up a network' wizard. This thing will be set up automatically. If it doesn't appear, or if you've already used this router, go to the Network and Sharing Centre and select 'Set up a new connection or network'. You'll then be taken through the steps.
On a Mac: Go to System Preferences, then Network, Built-In Ethernet, Advanced. This is where you'll find all the settings you need to set up a new network.
- Set up your Wi-Fi
If you want to build a wireless network, you should configure your router to get it.
If you only want computers to connect to the LAN via ethernet cable, go ahead and skip this step.
The router or network switch's manual will tell you how to configure Wi-Fi, so follow those instructions.
- Connect to the internet
A LAN is designed to connect different devices to each other - but if you want it to have internet access too, now's when you need to set it up.
If you already have a working router and broadband connection, you should just be able to plug in and go.
If you're setting up a new router and/or internet connection, you'll need to follow the instructions given to you by your broadband provider or router manufacturer.
Either way, you'll need to plug your router and modem into your home's main phone line, using the router's WAN port.
- Connect the rest of your devices
Whether you're connecting your gadgets to the LAN via Wi-Fi or ethernet cable, the time has come to get it all hooked up. These devices include other computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, TV set top boxes, games consoles, streaming sticks, etc.
To connect via Wi-Fi, turn on Wi-Fi on your device, and select your home network from the list.
Connecting with an ethernet cable is simpler - just plug one end into your network switch or router and the other into your devices.
- Get sharing
A LAN can help you share resources across it, such as devices, files, and media. With Windows PCs, you can create a 'Homegroup'.
Go to Control Panel, then Network and Internet, then Homegroup, and select 'Create a homegroup'. Windows will take you through the homegroup setup wizard and give you a password that other devices will need in order to connect to it. This is also where you can establish individual user accounts on your new LAN.
Now your home LAN has been built.
This Guide is from: https://www.broadbandchoices.co.uk/how-to/how-to-set-up-a-local-area-network.

Expertise Builds Trust
20+ Years • 200+ Countries • 21500+ Customers/Projects
CCIE · JNCIE · NSE7 · ACDX · HPE Master ASE · Dell Server/AI Expert